The secret to the Zone diet is reducing insulin resistance to achieve a better hormonal balance from your diet. This starts with having adequate protein at each meal. Protein is critical for success; you need a certain amount at each meal to induce satiety. That amount is approximately 30 grams of low-fat protein per meal. However, that amount of protein must still be balanced by the appropriate amount of carbohydrates to reduce insulin resistance. Then you add a dash of high-quality fat for flavor.
The Ideal Balance of a Zone Meal
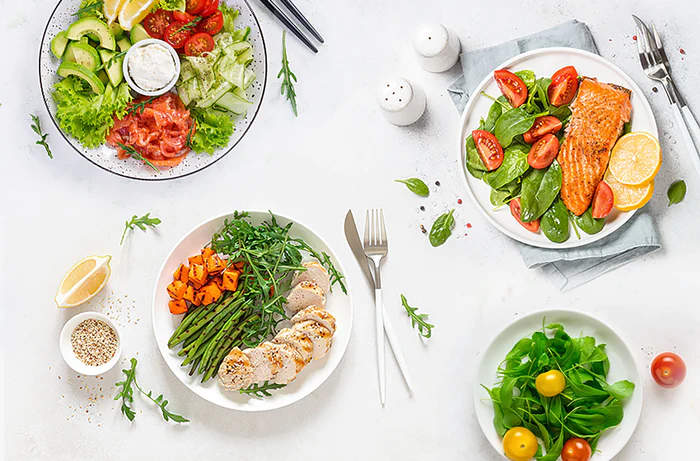
A Zone meal should contain approximately 400 calories to help stabilize blood sugar. Those 400 calories should contain at least 30 grams of protein, less than 12 grams of fat, and about 40 grams of net carbohydrates (total carbohydrates minus fiber) primarily from low-glycemic choices. Carbohydrates choices should ideally be rich in fiber and high in polyphenols to achieve better hormonal balance in the blood. If you can go 4-5 hours without hunger after a meal, you know that meal had the optimal Zone balance.
Your Guide to Making Zone Meals
Here we will take you through simple ways to make Zone meals. Every Zone meal starts with adequate protein for superior appetite control. The better the quality of your choices, the faster you will reduce insulin resistance. Here are some general tips for a Zone meal.
Start with Protein (approximately 30 grams per meal)
Your goal is to get about 30 grams of high-quality protein at each meal.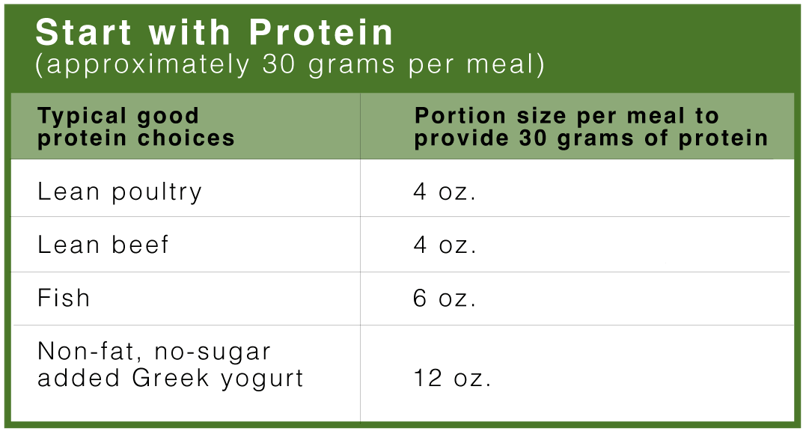

Add Carbohydrates
If you are making classic Zone meals, you want to add sufficient low-glycemic carbohydrates (such as non-starchy vegetables) to balance the protein at a meal. Low glycemic means the carbohydrates from these sources enter the blood as glucose at a slower rate. Protein is more uniform in its density, whereas carbohydrates are not. Non-starchy vegetables have a low carbohydrate density, meaning you must consume many more of these carbohydrates to get the same amount of glucose entering the blood as in a much smaller portion of starchy vegetables or grains. Here is an estimate of the portion size of each type of carbohydrate to get about 40 grams of net carbohydrates per meal.
Best carbohydrate choices for a Zone meal
These carbohydrates enter the blood as glucose slowly and are the best to reduce insulin resistance.
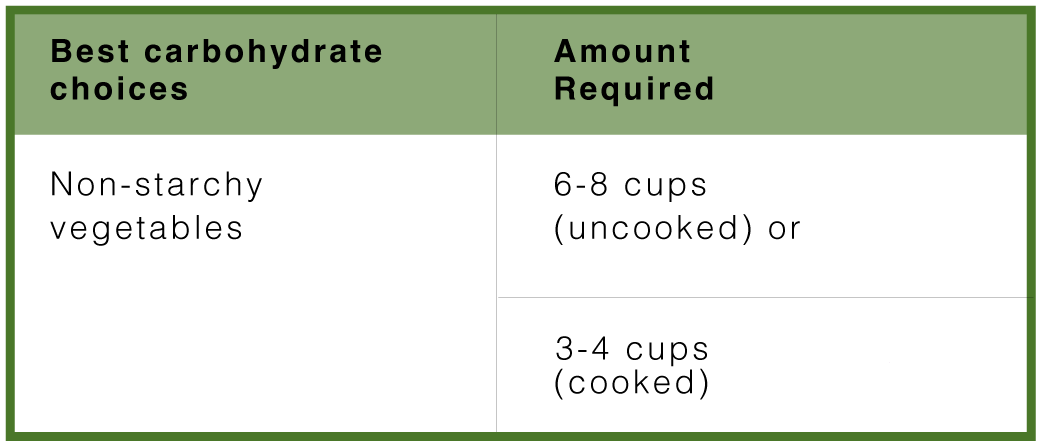
If you are using Zone PastaRx as your protein choice, you will only need to add 1 ½ to 2 cups of cooked vegetables to provide approximately 40 grams of carbohydrates at a meal to balance your protein intake.
The best choices for non-starchy vegetables would be the ABCs (asparagus, artichokes, broccoli, cauliflower, and spinach), as they have a better protein-to-carbohydrate ratio than other vegetables.
Less desirable carbohydrate choices
These carbohydrates are less desirable as they enter the bloodstream as glucose at a faster rate and will not be as effective in reducing insulin resistance. However, if you want to use these carbohydrates to replace one quarter of the preferred carbohydrate choices for a Zone meal, here are the levels you can use (choose only one).
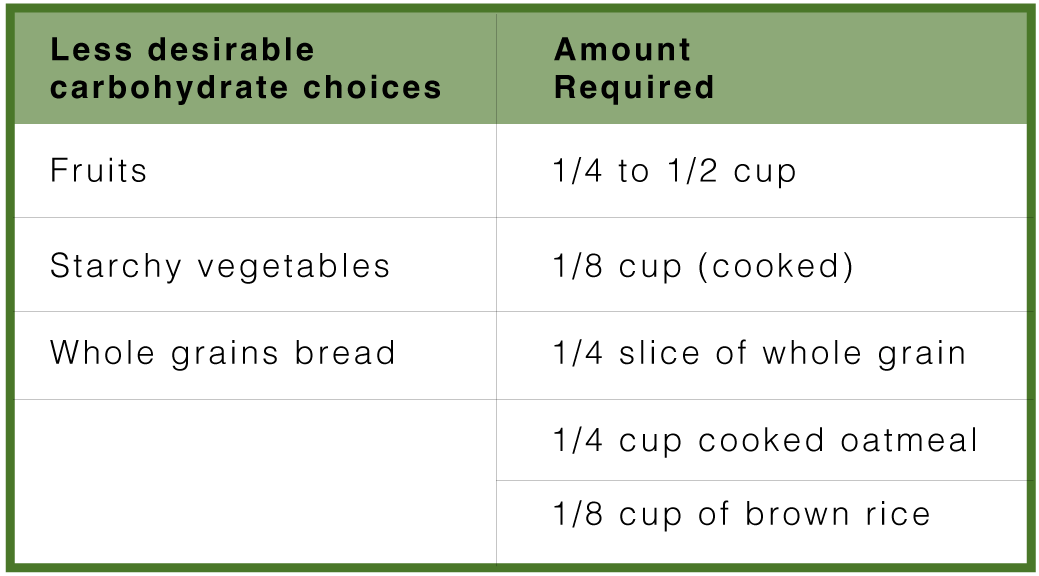 You can also see that trying to balance your protein portion at a Zone meal using more than these fractions of fruits, whole grains or starchy vegetables will have a decreased effect on reducing insulin resistance because they rush into the blood as glucose at a much faster rate than preferred non-starchy vegetables.
You can also see that trying to balance your protein portion at a Zone meal using more than these fractions of fruits, whole grains or starchy vegetables will have a decreased effect on reducing insulin resistance because they rush into the blood as glucose at a much faster rate than preferred non-starchy vegetables.
Poor carbohydrate choices include white carbohydrates (bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes) as they contain no polyphenols (that’s why they are white) and enter the blood quickly as pure glucose, thus increasing insulin resistance. Therefore, these carbohydrates should not be part of the diet for anyone with a higher level of insulin resistance. On the other hand, the use of Zone PastaRx as a rice or pasta replacement has been shown in clinical trials to reduce insulin resistance.
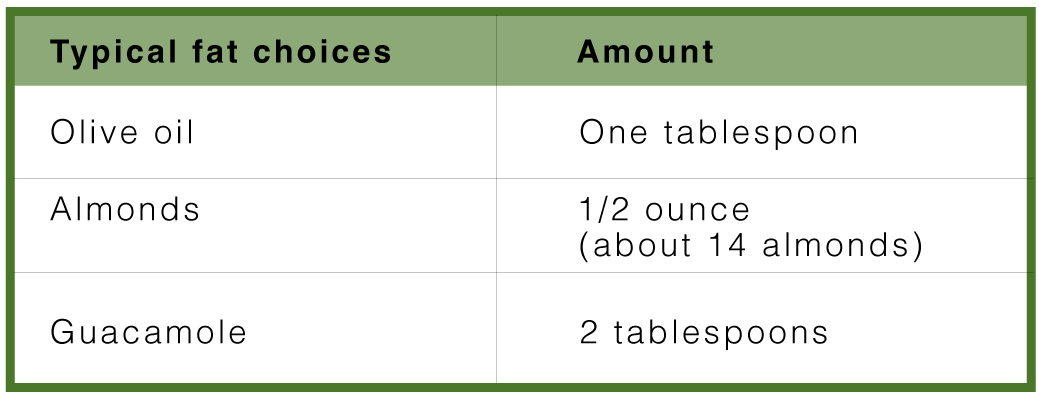
Add Fat
The last thing you add to your meal is fat. However, just enough for improved taste because too much fat provides excess calories that will slow down your rate of reducing insulin resistance. You only need one portion of fat per meal providing about 12 grams.
Putting It Together
A typical Zone meal should supply about 30 grams of protein, approximately 40 grams of carbohydrates, and about 12 grams of fat. This gives you a protein-adequate meal with moderate levels of low-glycemic carbohydrates and low amounts of healthy monounsaturated fat providing approximately 400 calories per meal. The result of that balance is a lack of hunger or mental fatigue for the next five hours because of better hormonal control of satiety and improved blood sugar levels.
When To Eat Your Zone Meals
Here is the basic science behind meal timing:
- Eat your first Zone meal within an hour after waking up.
- Consume three Zone meals of equal calories to control hunger throughout the day. Each Zone meal should contain about 30 grams of protein.
- Eat your protein first at every meal to maximize hunger suppression.
- Eat your last Zone meal before sunset or at least four hours before bed.
Your metabolism is controlled by circadian rhythms determined by sunlight, meaning you want to spread your calorie intake evenly throughout the daylight hours. Your goal is to work with your metabolism to reduce insulin resistance, not against it.






Let Us Know What You Thought about this Post.
Put your Comment Below.